What is Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol?
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a network protocol that enables a server to automatically assign an IP address to a computer from a defined range of numbers (i.e., a scope) configured for a given network. This allows devices to communicate with each other and access resources on the network, such as the internet.
The DHCP server maintains a record of IP addresses that have been assigned, along with other information such as the subnet mask, default gateway, and DNS server. When a device connects to the network, it sends a broadcast request for an IP address, and the DHCP server responds with an available IP address from the scope, along with the other required configuration settings. This process is known as “DHCP lease.” The lease has a expiration time, after which the device must request a new lease to continue using the same IP address or be assigned a new one.
A DHCP server can also provide some other parameters, such as:
- subnet mask
- default gateway
- domain name
- DNS server
Cisco routers can be configured as both DHCP client and DHCP server.
DHCP DORA Process
The DHCP process, also known as the DHCP handshake or DORA (Discover, Offer, Request, Acknowledge), involves four messages that are exchanged between a client and a server. The process goes as follows:
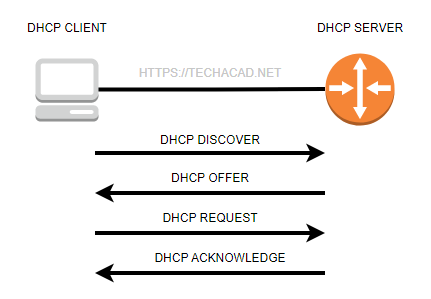
- DHCPDISCOVER: When a client device connects to a network, it sends a broadcast message to locate a DHCP server. This message contains the client’s MAC address and is sent to the broadcast address of the local subnet.
- DHCPOFFER: The DHCP server responds to the DHCPDISCOVER message by sending a DHCPOFFER message, which includes an available IP address and other configuration settings, such as the subnet mask, default gateway, and DNS server.
- DHCPREQUEST: The client device responds to the DHCPOFFER by sending a DHCPREQUEST message, which requests the offered IP address and configuration settings. The client may receive multiple DHCPOFFER messages from multiple servers, and it will choose the one it prefers and send a DHCPREQUEST message for that offer.
- DHCPACK: If the requested IP address is available and the configuration settings are acceptable, the DHCP server sends a DHCPACK message to confirm the assignment of the IP address and other configuration settings to the client. If the requested IP address is not available or the configuration settings are not acceptable, the DHCP server sends a DHCPNAK message to reject the request.
This process is known as the “DHCP discovery” or “DHCP exchange” process, and it is usually completed within a few seconds. After the DHCPACK message is received, the client is configured with the assigned IP address and other configuration settings and can communicate with other devices on the network.

